PCR and peptide based PCMV detection in pig - development and application of a combined testing procedure differentiating newly from latent infected pigs
Nicole Fischer1, Barbara Gulich1, Barbara Keßler2, Matthias Längin3, Jay A. Fishman4, Eckhard Wolf2, Klaus Boller5, Ralf R. Tönjes1, Antonia W. Godehardt1.
1Division of Haematology, Cell- and Gene Therapy, Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, Langen, Germany; 2Institute of Molecular Animal Breeding and Biotechnology, Gene Center, LMU Munich, Munich, Germany; 3Department of Anesthesiology, LMU Munich, Munich, Germany; 4Transplant Infectious Disease and Compromised Host Program, MGH Transplantation Center; Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, United States; 5Division of Immunology, Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, Langen, Germany
Introduction: Porcine cytomegalovirus (PCMV) is widely distributed in pigs and difficult to detect due to latency. PCMV infection of source pigs was associated with early graft failure after cardiac and renal xenotransplantation into nonhuman primates. Importantly, PCMV infection of the first genetically modified pig heart into a human may have contributed to the reduced survival of the patient. Sensitive and reliable assays for detection of latent PCMV infection are thus indispensable.
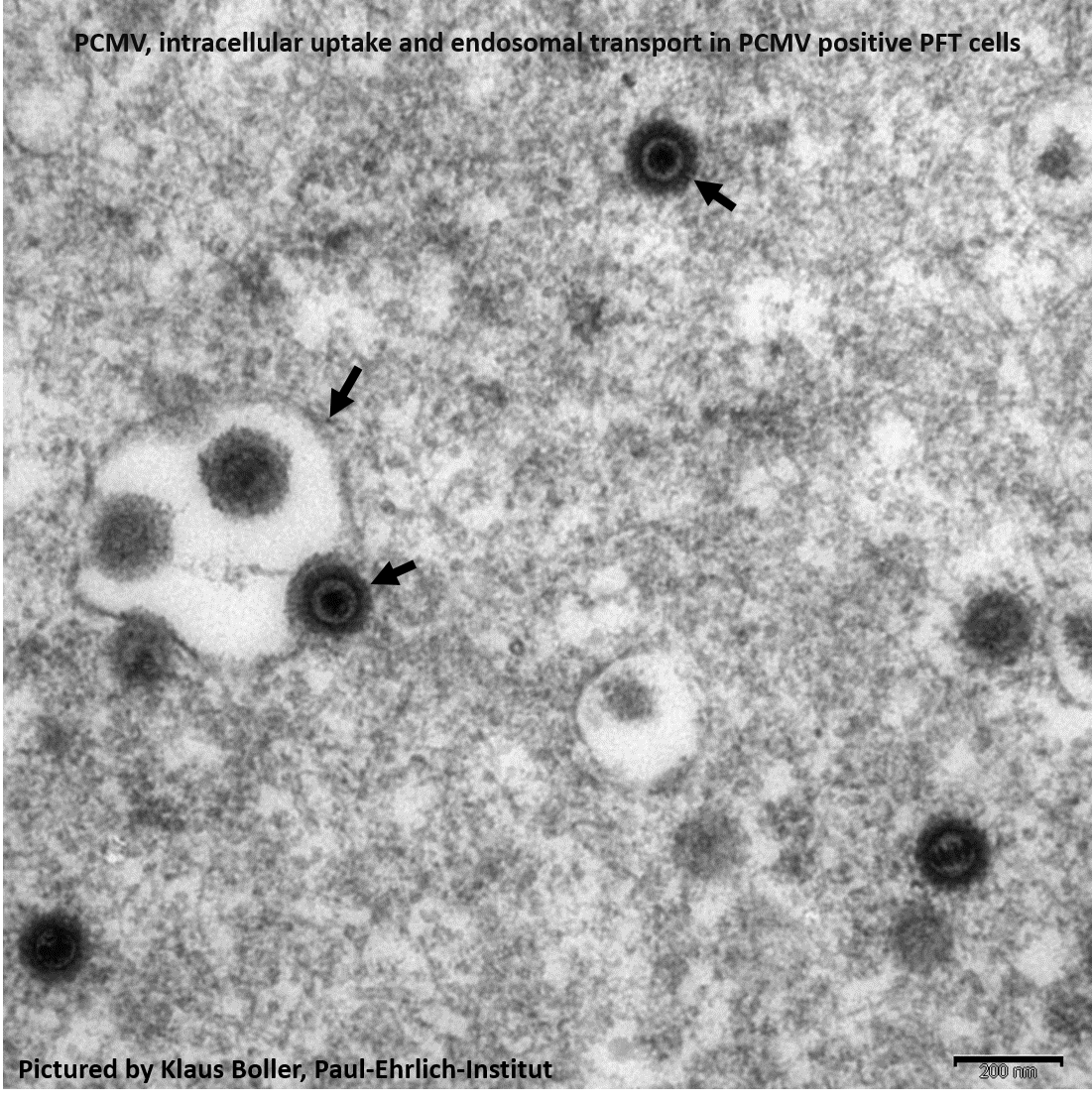
Method: Here, we report the development of five peptide-induced rabbit antisera specific for PCMV glycoprotein B (gB) and their validation for detection of PCMV in infected pig fallopian tube (PFT) cells by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. The anti-gB antibodies were also used for detection by Western blot analysis of PCMV purified from the supernatant of infected PFT cells. Sera of infected vs. non-infected pigs have been compared. In parallel, PCMV viral load in blood samples of the animals was quantified by a novel highly sensitive nested-PCR and qPCR assay. A combination of four partly overlapping peptides from the gB C-terminus was used to establish a diagnostic ELISA for PCMV gB specific pig antibodies which is able to differentiate infected from non-infected animals and to quantify maternal antibodies in neonates.
Results: The combination of a highly sensitive nested PCR for direct virus detection with a sensitive peptide-based ELISA detecting anti-PCMV gB-antibodies, supplemented by Western blot analysis and/or immunohistochemistry for virus detection will reliably differentiate pigs with active infection, latently infected pigs, and non-infected pigs. It may significantly improve the virologic safety of xenotransplantation.
This work was supported by grant SFB TRR CRC 127: “Biology of xenogeneic cell and organ transplantation‐from bench to bedside” from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG, Bonn, Germany..