Incidence of serum antibodies to xenoantigens on triple-knockout pig cells in different human groups
Songzhe He1, Tao Li1, Hao Feng2, Jiaxiang Du3, David K.C. Cooper4, Hidetaka Hara6, Hongtao Jiang1, Dengke Pan5, Gang Chen2, Yi Wang1,7.
1Department of Kidney Transplantation, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou, People's Republic of China; 2Institute of Organ Transplantation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, People's Republic of China; 3Chengdu Clonorgan Biotechnology Company, Chengdu, People's Republic of China; 4Center for Transplantation Sciences, Department of Surgery, Massachusetts General Hospital/Harvard Medical School, Boston, United States; 5Clinical Immunology Translational Medicine Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu, People's Republic of China; 6College of Veterinary Medicine, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming, People's Republic of China; 7Second Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang, People's Republic of China
Background: Xenoantigens other than Gal, Neu5Gc, and Sda may be playing a role in pig graft rejection. We investigated the incidence of antibodies to unknown pig xenoantigen in different human groups.
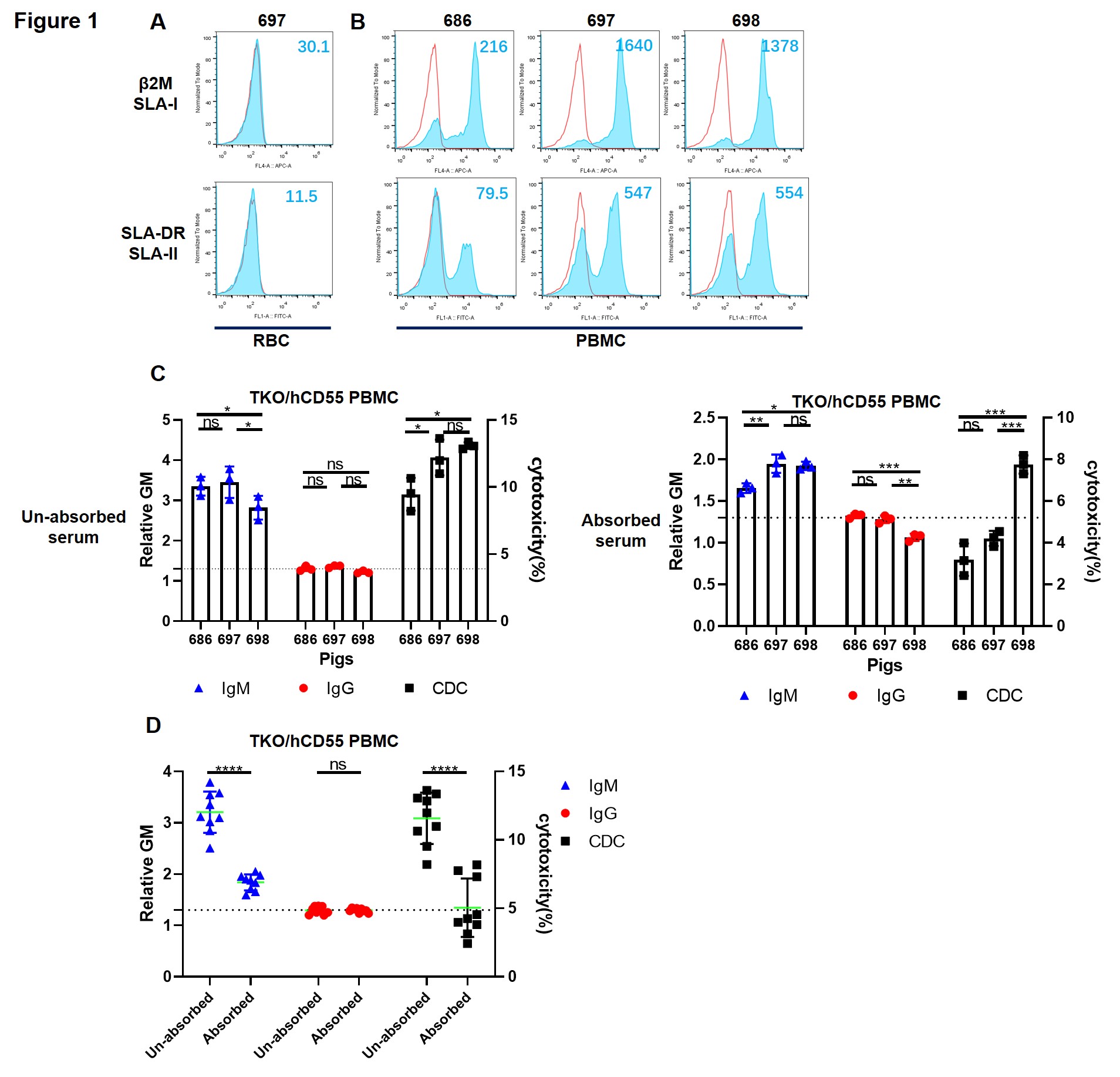
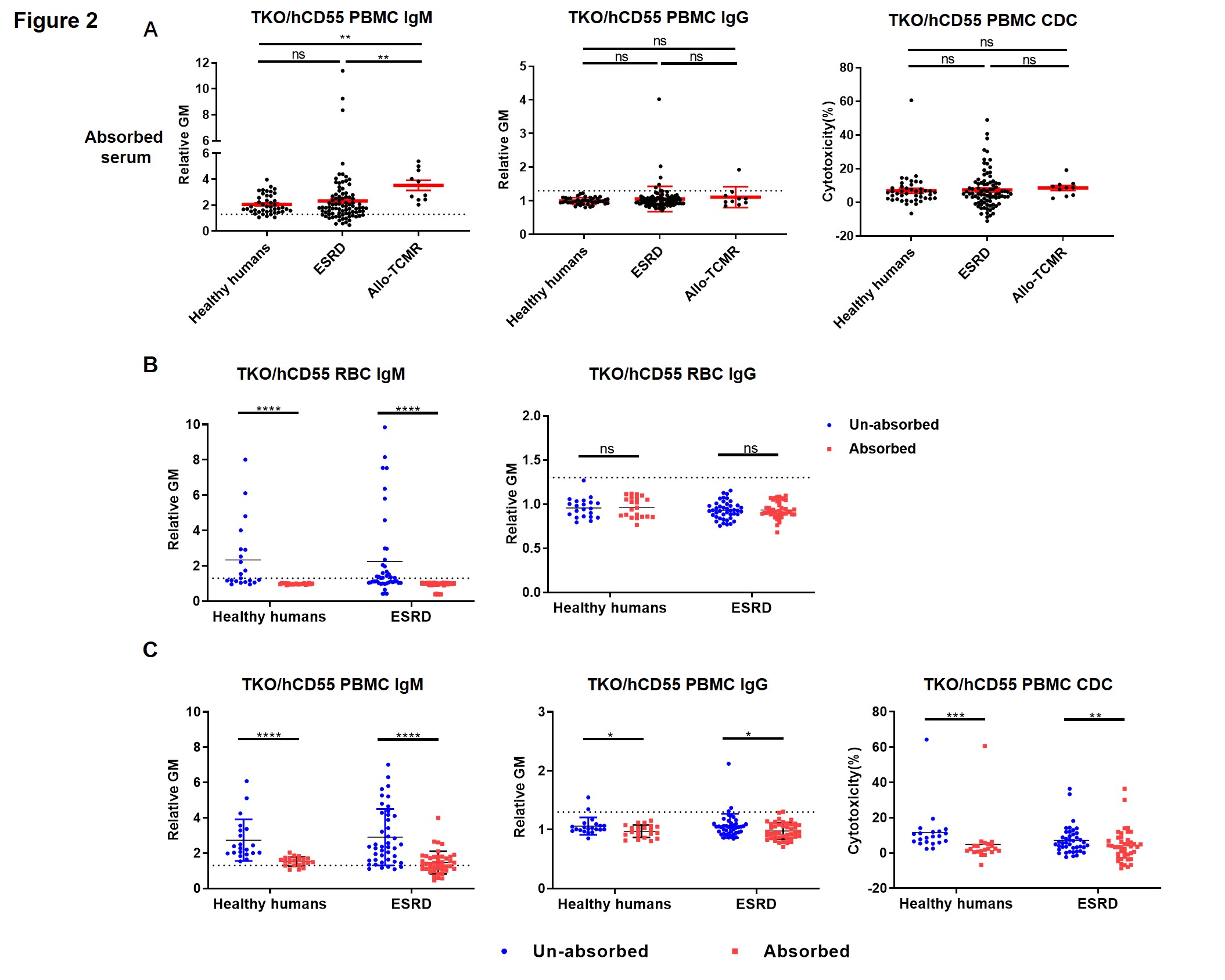
Methods: We collected blood from TKO/hCD55 pigs (n=3), and isolated PBMCs and RBCs. Serum samples were collected from(i) healthy volunteers (n=43), (ii) patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (n=87), and (iii) renal allotransplant recipients who were currently experiencing T cell-mediated rejection (allo-TCMR, n=10). The sera were initially incubated with TKO/hCD55 pRBCs to absorb anti-pig antibodies (except against SLA and possibly other antigens not expressed on pRBCs) and then the serum (absorbed or unabsorbed) was tested for antibody binding and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) to TKO/hCD55 pig PBMCs.
Results: A significant reduction in IgM/IgG binding and CDC was observed in the absorbed sera. The SLA expression is difference in each pig. IgM antibodies (but rarely IgG) against unknown xenoantigens expressed on TKO/hCD55 PBMCs, possibly against SLA, were documented in healthy humans, patients with ESRD, and those with renal allografts undergoing acute T cell rejection. IgM (but not CDC) was higher in patients experiencing allo-TCMR.
Conclusions: Human sera contain IgM antibodies against unknown pig xenoantigens expressed on TKO/hCD55 pPBMCs. Although not confirmed in the present study, the targets for these antibodies may include swine leukocyte antigens.
the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82260154). Major Scientific and Technological Project of Hainan province (ZDKJ2019009) . Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (820RC766, 821QN413).