Clinical subjects may suitable for renal xenotransplantation because of lower anti-pig antibodies
Tao Li1, Hao Feng2, Jiaxiang Du3, Hongtao Jiang1, Songzhe He1, Dengke Pan3, Gang Chen2, Yi Wang1.
1Department of Organ Transplantation, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou, People's Republic of China; 2Institute of Organ Transplantation, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, People's Republic of China; 3Clinical Immunology Translational Medicine Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu, People's Republic of China
Kidney xenotransplantation is expected to contribute to resolving the shortage of kidneys from deceased human donors. Although progress in experimental life-supporting pig renal xenotransplantation has been encouraging, there are still issues to be considered before a clinical trial can be initiated. We attempted to clarify some of these by an in vitro study.
Blood was drawn from healthy volunteers (Volunteers, n=20), patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD, n=20), and renal allotransplant recipients who were currently experiencing T cell-mediated rejection (Allo-TCMR, n=20). Serum IgM/IgG binding to, and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) of, PBMCs and RBCs from (a) wild-type (WT), (b) α1,3-galactosyltransferase gene-knockout (GTKO), (c) GTKO/beta-1,4-N-acety1 galactosaminyltransferase 2-knockout (GTKO/β4GalNT2KO), (d) GTKO/cytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase-knockout (GTKO/CMAHKO), and (e) GTKO/β4GalNT2KO/CMAHKO /hCD55 (TKO/hCD55) pigs were measured by flow cytometry.
We obtained the following results: (i) Serum IgM/IgG binding and CDC in Volunteers were significantly greater to WT, GTKO, and GTKO/β4GalNT2KO PBMCs or RBCs than to GTKO/CMAHKO and TKO/hCD55 cells; (ii) In all sera, the lowest antibody binding and CDC were to GTKO/CMAHKO and TKO/CD55 pig cells.
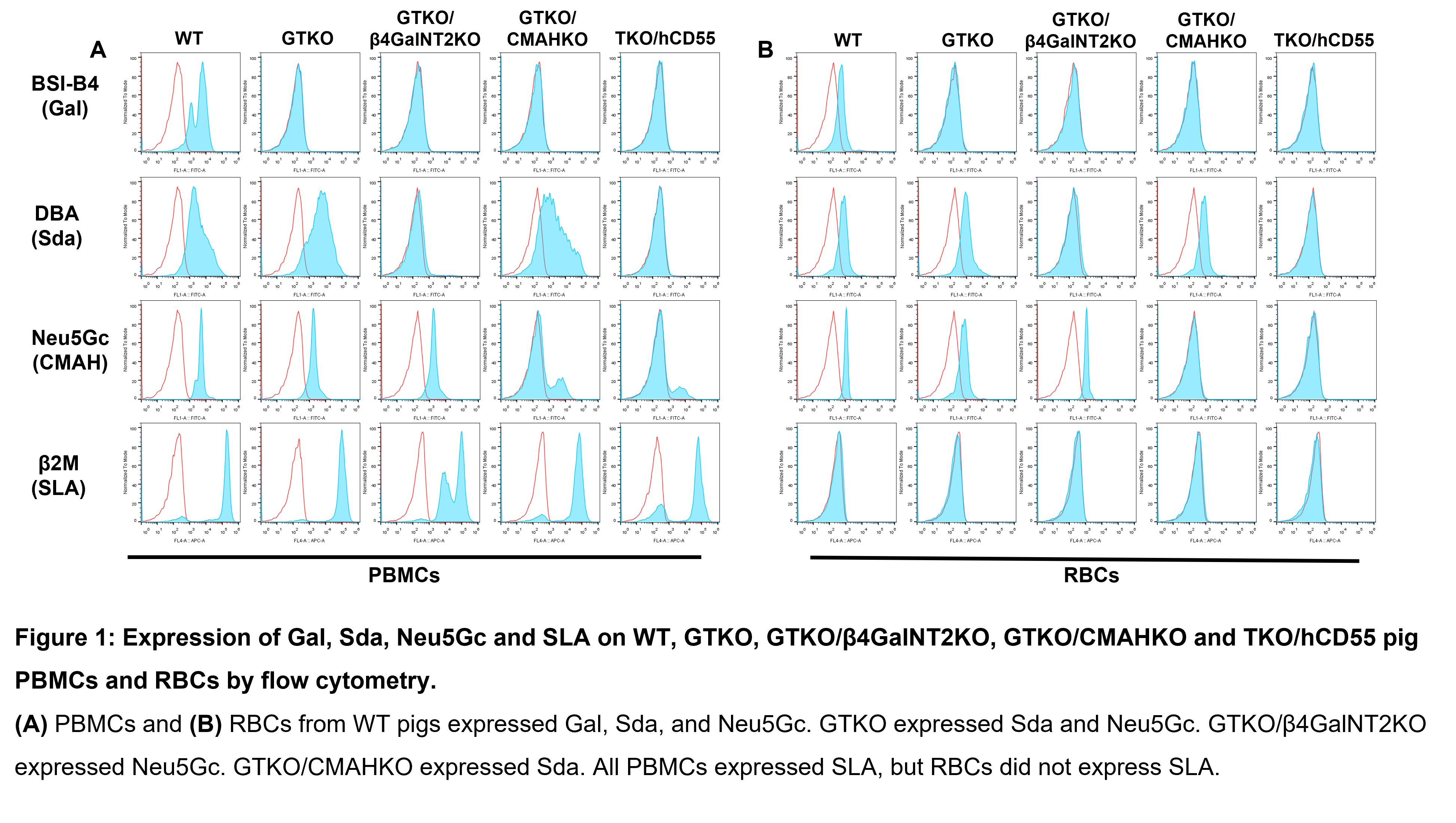


We conclude (i) subjects with ESRD, or who are immunosuppressed after kidney allotransplantation, have lower levels of antibody binding and CDC to genetically-engineered pig cells than do volunteers; (ii) TKO pigs with selected human ‘protective’ transgenes, e.g., CD55, are likely to prove to be the optimal sources of kidneys for clinical xenotransplantation.
This study was supported in part by the Major Scientific and Technological Project of Hainan province (ZDKJ2019009) and Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (821QN413). .